Different locations have different costs of setting up a facility. These costs can be classified into two types:
-
Fixed cost: it can be the cost of land, construction, etc.
-
Variable cost: it can be the cost of labor, raw materials, etc.
Let us understand these two terms with the help of a graphical representation.
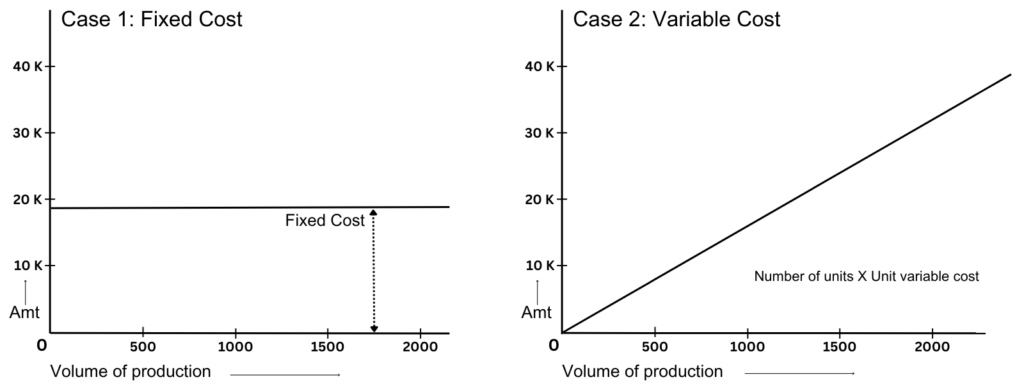
Total cost = Fixed cost + Variable cost.
After manufacturing, you’ll be selling the goods at a certain price. Number of units * Cost of each unit = Total revenue. Following is the representation of the total cost and total revenue by a graph.
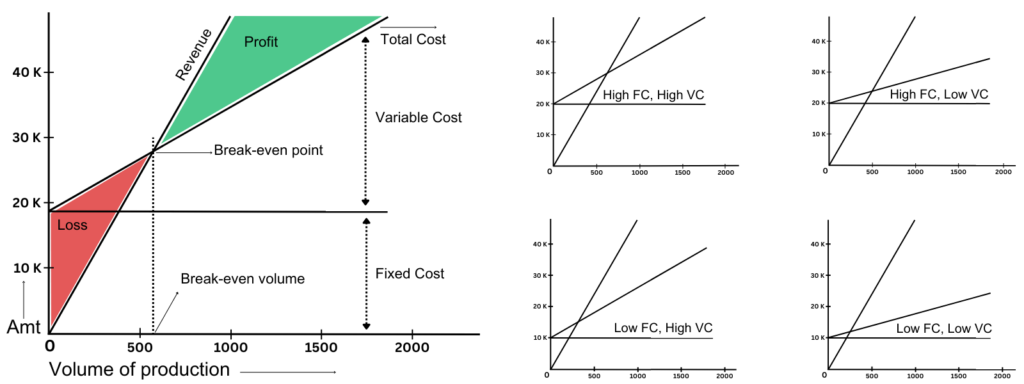
The lowest break even point means that the facility will become profitable faster compared to other locations. So, preference would be given to a location that has the lowest break even point. Looking at the variations of fixed and variable costs from the graph, it is clear that the fourth location will be preferred by companies to become profitable quickly.
Facility location planning using the center of gravity method:
Facility location decisions are examples of strategic capacity planning. Let us understand the center of gravity method in operations management using an example.
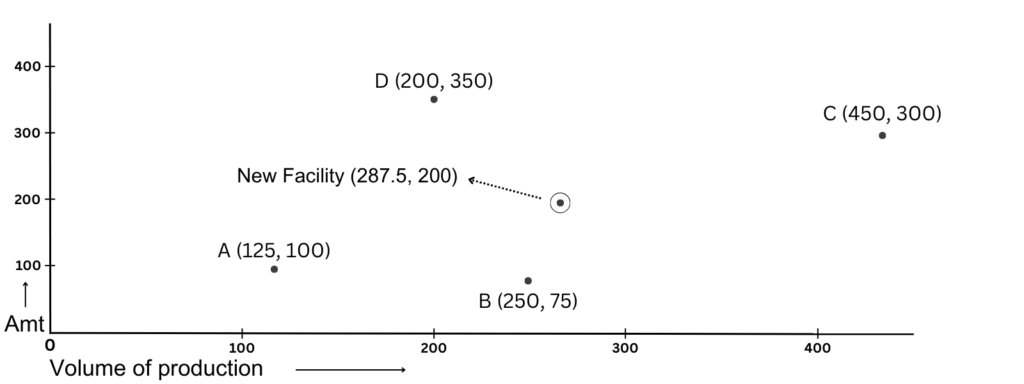
Example: The Mumbai baking company currently has four retail locations within the metropolitan area of the city. Currently, each retail outlet makes all of its breads and pastries from scratch. In order to reduce costs and ensure consistency of the firm’s products across all locations, the management has decided to build a central commissary where the products will be prepared and subsequently distributed to the four retail stores. The question now is where to locate the commissary.
|
Store location |
X coordinate |
Y coordinate |
Quantity/ Volume of products sold |
|
A |
125 |
100 |
1250 |
|
B |
250 |
75 |
3000 |
|
C |
450 |
300 |
2750 |
|
D |
200 |
350 |
1500 |
The criteria for choosing the location of the commissary would be a place where the total cost of transportation to all four store locations is minimal. Now, we have been given the X and Y coordinates of these locations, and the volume of products sold is also given. Where does it make sense to locate this commissary?
Let’s understand what the center of gravity method is. It is a quantitative technique that can be used to determine the optimal location of a facility based on minimizing the transportation cost between where the goods are produced and where they are distributed.
Center of gravity method formula:
- Locate each of the existing facilities on X and Y coordinate grid map.
- Find the X and Y coordinates of the new plant by taking the weighted average of X and Y coordinates of all the existing facilities.
x0 = ∑xiLi/∑Li and y0 = ∑yiLi/∑Li
Where; x0, y0 are the coordinates of the new facility; xi, yi are the coordinates of existing facilities and Li is the load to be transported from the new facility to the existing locations.
Coming back to the example,
Step 1: Plot the graphs as per the coordinates
Step 2: X0 = ((125 × 1250) + (250 × 3000) + (450 × 2750) + (200 × 1500))/((1250 + 3000 + 2750 + 1500)) = 287.5
Y0 = ((100×1250) + (75 × 3000)+(300 × 2750) + (350 × 1500))/((1250 + 3000 + 2750 + 1500)) = 200
Factor rating method in operations management:
In this method, first the relevant location factors for the company are selected. Let’s say that the manufacturing company is selecting the ideal location for their next factory. So first they will have to review all the factors that can affect the facility location decision and then shortlist the factors that are relevant to them.
Let’s say they have come up with the following factors like close proximity to the market and raw materials, good transportation facility, availability of power supplies, inexpensive skilled labor, rebate taxes, availability of cheap land.
|
Weightage |
Kanpur |
Chennai |
Ahmedabad |
|
5 |
1 |
5 |
4 |
|
20 |
5 |
1 |
3 |
|
15 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
|
10 |
2 |
4 |
1 |
|
15 |
4 |
3 |
5 |
|
15 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
20 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
So, these are known as the factor location ratings. Now we have to find out the products of the location ratings.
|
Weightage |
Kanpur |
Chennai |
Ahmedabad |
|
5 |
5 |
25 |
20 |
|
20 |
100 |
20 |
60 |
|
15 |
45 |
45 |
30 |
|
10 |
20 |
40 |
10 |
|
15 |
60 |
45 |
75 |
|
15 |
15 |
30 |
30 |
|
20 |
60 |
20 |
60 |
|
Total |
305 |
225 |
285 |
From the above example, Kanpur seems to be the most favorable location. Different companies need different types of facilities to run their organizations. A manufacturing company would have factories or plants to manufacture the goods, warehouses or distribution centers to store the goods, and offices to run their supporting functions. In the service sector, such as courier companies, banks, insurance companies, the offices are their facilities.